Access
Getting an account
Getting an account and using NU HPC facilities is free of charge for all NU faculty, research assistants, and students. However, opening an account for a research assistant or student requires sponsorship/authorization by their PI (Principal Investigator of a research project; typically a faculty member or head of a lab). Therefore, no accounts will be created at the direct request of a student or RA. The procedure must be initiated by the PI. It is assumed that the PIs take full responsibility for the proper use of the HPC facilities by their group members and their compliance with basic cybersecurity rules.
Below are step-by-step instructions for PIs to request new accounts for themselves and their group members. Please be aware that all users must have a valid nu.edu.kz corporate email address.
- To create a new group on Shabyt cluster, under which group member accounts may be added later, the PI should fill out the corresponding form in the ticketing system. Instructions for creating a request in the ticketing system can be found here. If, at the time of filling out this form, the PI already knows who of his group members need accounts on Shabyt, he/she can indicate the names, emails, and positions of those people right in the form. Please note that the form must be filled by the PI only, regardless of the fact who the accounts are for and how many of them need to be created. Group members cannot request accounts by themselves.
- NU HPC team will process the application form and approve/reject it based on the information provided.
- If/when the application is approved, a username, temporary password, and first time login instructions will be communicated by the HPC administrator to each new user.
- Having the credentials received from the HPC admins, users should connect to the cluster(s) where they have accounts by means of the SSH (secure shell) protocol. No other connection type is supported. Copying files to/from the cluster(s) can be done either via SFTP (secure ftp) or SCP (secure copy) command.
- The PI assumes full responsibility for the use of the HPC systems by his/her group members. If the PI cannot take such a responsibility then he/she should not request accounts for group members.
- In the case if there is a need to add or remove a group member account under a specific PI after the initial setup (after the form was filled), the PI should contact HPC admin via email hpcadmin@nu.edu.kz. If a new accounts are to be added, the PI must provide all necessary information (name, email, position) about the new group members.
Access instructions
Important note: Only connections that originate from the internal campus network are allowed at this time. The HPC team may implement a secure mechanism for outside connections in the future. Until then the out-of-campus users must use VPN (virtual private network) to enable connectivity to NU HPC facilities. This requires downloading and installing GlobalProtect VPN software for this purpose. Please go to NU Help Desk and search for VPN. There should be a form that requests VPN access by NU employees and RAs (an approval by the PI might be required). Read the corresponding instructions, which are also available there. Note that NU VPN policies might change with time. Also note that NU HPC team does not manage VPN access and is not responsible for its operation. For any issues and inquiries regarding VPN please contact NU Help Desk directly by submitting a ticket through their ticketing system.
The VPN access is necessary only if you are outside of the NU campus. If you connect from campus you do not need to use any VPN software (in fact, you will not be able to).
When a user is on campus or is connected to the campus network via VPN, he/she should use an SSH client to establish a connection with the interactive login/management node (IP address 10.3.64.61). There is a multitude of free and powerful third-party SSH clients available for any operating system. Moreover, Windows, Linux, and MacOS all have native SSH clients built directly into the command line. For example, in Windows, one can just launch the command prompt (cmd.exe) and initiate an SSH session from there. If you wish to use a SSH client with a graphical user interface on Windows, we can recommend PuTTY, which can be downloaded from here.
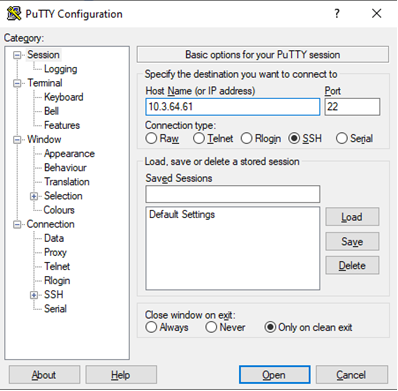
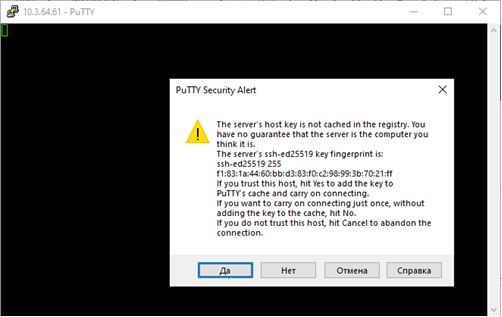
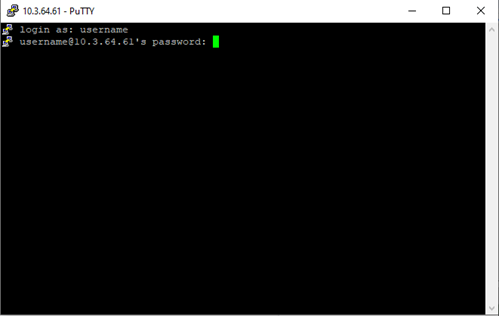
Windows (PuTTY) Download, install, and launch the PuTTY client. Next, in the PuTTY configuration window that pops up, enter 10.3.64.61 (this is the IP address of Shabyt login node) in the field Host Name. Make sure the Connection type field is set to SSH. Then press the Open button. When you connect for the very first time, PuTTY will show a security alert. Accept it by pressing Yes. Then enter your login and password (use the credentials provided by the HPC administrators) as requested in the terminal window that opens up.
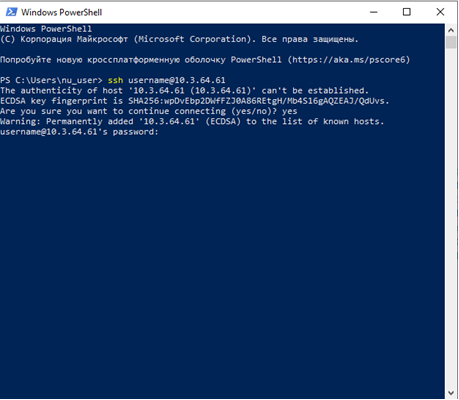
Windows (PowerShell or Command Prompt) Windows PowerShell and Command Prompt provide a built-in SSH client. Search for the PowerShell or Cmd app and launch it. Then enter your credentials.
UNIX Compatible OS Every Linux distribution comes with an OpenSSH client that should be installed by default. Thus, there is no need to install any additional software packages. Simply locate and launch a Terminal. At the prompt of the terminal window enter `ssh username@10.3.64.61' (replace username with your actual user name). It will ask you for your password. Note that you will not see any characters on the screen as you type the password. This is normal. When you connect for the very first time you will also be prompted to confirm the authenticity of the host. Type yes to confirm it.
Environment Modules Environment Modules is a software tool that simplifies modifying the shell environment for users. It is especially useful in systems where software packages have multiple versions or configurations. It allows multiple versions of the same software package to be installed simultaneously and invoked by simply loading a proper module.
Here is a list of most frequently used terminal commands implemented in Environment Modules: - `module avail`: List all software modules available in the system via Environment Modules - `module show <ModuleName>`: Display information about module file - `module load <ModuleName>`: Load module into the shell environment - `module unload <ModuleName>`: Remove module from the shell environment - `module list`: List currently loaded modules - `module purge`: Unload all previously loaded modules
To learn about other commands please type `man module` in the terminal window.